Key Challenges for Data Centers

Revamping Power & Cooling for AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) workloads are demanding more processing power and requiring more energy efficient cooling systems. Data centers are faced with the challenge of revamping their infrastructure to support these new demands.

Utility Grids Struggle with Data Center Demands
Traditional utility grids were not designed to handle the massive energy demands of data centers. This can lead to power outages and grid instability, impacting data center operations.
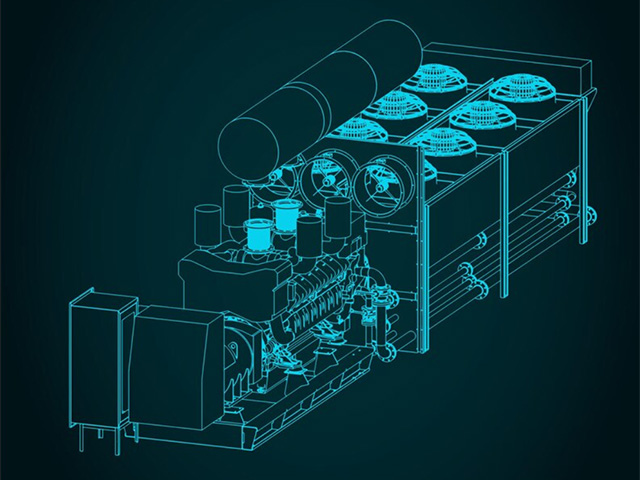
Replacing Outdated Diesel Generators
Many data centers rely on diesel generators for backup power, but these are becoming increasingly outdated and unreliable. Additionally, they contribute to environmental pollution and can be costly to maintain.
Revamping Power and Cooling for AI
Increased Compute Demands
AI workloads are highly compute-intensive, requiring substantial processing power and cooling capacity.
Energy Efficiency Challenges
Optimizing power and cooling for AI workloads while maintaining energy efficiency is crucial to minimize operational costs and environmental impact.
Advanced Cooling Technologies
Data centers are exploring innovative cooling solutions, such as liquid immersion cooling and precision air conditioning, to address AI's heat dissipation requirements.
Utility Grids Struggle with Data Center Demands
Traditional utility grids were not designed to handle the massive energy demands of modern data centers. They lack the capacity and flexibility to meet the growing needs of these energy-intensive facilities.
The grid's infrastructure, including transformers and power lines, may not be able to handle the high power requirements of data centers. This can lead to voltage fluctuations and power outages, which can disrupt operations and data processing.
Replacing Outdated Diesel Generators
Diesel generators have been a mainstay of data center backup power for decades. However, they are increasingly seen as outdated and unsustainable. These generators are noisy, polluting, and require significant maintenance. They are also prone to breakdowns, which can lead to costly downtime. As data centers move toward more sustainable and reliable power sources, diesel generators are being replaced with more modern alternatives.
Modern alternatives to diesel generators include battery energy storage systems, fuel cells, and microgrids. These technologies offer several advantages over diesel generators, including lower emissions, higher efficiency, and greater reliability. Battery energy storage systems can provide short-duration backup power during outages, while fuel cells and microgrids can provide long-duration backup power or even serve as a primary power source.
Increased Costs, Emissions, and Downtime Risks
Increased Costs
Higher energy bills, inefficient cooling, and outdated infrastructure contribute to escalating expenses.
Higher Emissions
Traditional power sources like diesel generators generate significant carbon emissions, harming the environment.
Downtime Risks
Outdated or unreliable infrastructure can lead to unexpected outages, disrupting operations and causing financial losses.
The Solution: A Smart Distribution Grid
Enhanced Efficiency
DCGRIDS optimize energy usage by intelligently managing power flows, reducing waste and lowering operational costs.
Increased Reliability
DCGRIDS build resilience by integrating diverse energy sources, ensuring uninterrupted operations even during outages.
Sustainable Operations
DCGRIDS facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, reducing carbon footprint and promoting sustainability.
Diverse Energy Resources (DERs) as Grid Elements
Natural Gas and Solar Power
Natural gas provides reliable baseline power generation with lower emissions than coal, while solar arrays deliver clean, renewable energy during peak daylight hours. These complementary sources form a strong foundation for the energy mix.
BESS and Traditional Grid
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) provide critical power smoothing and backup capabilities, while connection to the traditional power grid ensures continuous power availability and helps manage peak loads. This hybrid approach maximizes reliability and efficiency.
Microgrid Architecture Enables Resilience
-
01
Decentralized Power
Microgrids operate independently of the main grid, ensuring continuous power supply even during outages.
-
02
Redundant Power Sources
Multiple DERs and energy storage systems provide backup power, minimizing downtime.
-
03
Enhanced Reliability
Microgrids isolate critical data center operations from grid disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted service.

DCGrids utilize a microgrid architecture, which enhances the resilience of data centers by creating a self-sufficient power system. This microgrid approach provides multiple layers of protection, ensuring uninterrupted operations even in the event of disruptions to the main utility grid.
Diversified Renewable Energy Integration

Natural Gas
Leveraging solar panels on rooftops and parking lots to generate clean energy for data centers.
Solar
Utilizing efficient natural gas systems as a reliable baseline power source with lower emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels.
SMR (Small Modular Reactors)
Implementing advanced nuclear technology through small modular reactors for consistent, carbon-free power generation.
Geothermal
Utilizing geothermal energy in regions with geothermal activity for sustainable energy production.
AI-Powered Micro Grid Control System
DCGrids leverages advanced artificial intelligence to create an intelligent control system that optimizes data center operations in real-time.
Data Collection & Analysis
AI continuously monitors CPU load, memory usage, network bandwidth, and power consumption patterns across all systems.
Intelligent Decision Making
Advanced algorithms process operational data to make smart decisions about resource allocation and energy distribution.
Dynamic Load Balancing
Workloads are automatically distributed across servers based on AI-optimized performance metrics and energy efficiency targets.
Adaptive Power Management
Smart control systems dynamically adjust power consumption by managing server utilization and responding to real-time electricity rates.
Automated Grid Analytics and Controls
-
Real-time Monitoring
DCGrids continuously monitors energy consumption, generation, and grid performance, providing real-time insights into system operations.
-
Predictive Analytics
Advanced algorithms analyze historical data and current conditions to anticipate future energy needs and optimize grid operations for efficiency and stability.
-
Automated Control
DCGrids automatically adjusts energy flows, manages DERs, and optimizes power distribution, reducing manual interventions and ensuring optimal grid performance.

Predictive Maintenance for Grid Assets

DCGrids leverage data analytics to monitor the health of grid assets, such as solar panels, batteries, and inverters, in real-time. By analyzing performance trends and identifying potential issues early on, DCGrids can proactively schedule maintenance tasks before equipment failures occur. This minimizes downtime, reduces maintenance costs, and extends the lifespan of critical grid components.
Enhanced Cybersecurity for the Grid
Network Segmentation
Isolate critical infrastructure from external networks, limiting the impact of attacks.
Threat Intelligence & Monitoring
Proactively identify and mitigate potential threats using real-time monitoring and analysis.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Secure access to sensitive data and systems with additional layers of security.
Regular Security Audits
Identify vulnerabilities and implement corrective actions to ensure ongoing security.
Let’s Build the Future Together
Partner with Infrakey to transform your data infrastructure.
